Within the context of new-age project development, the majority of enterprises in the software industry have moved towards advanced methodologies such as Agile and DevOps to reduce testing turnaround time and fasten the product’s time-to-market. This also means automation testing tool is gradually replacing Manual Testing and has become one of the dominant methods in the testing process. Moreover, The Global Marketing Insights report also indicates that the market size for Automation Testing surpassed USD 15 billion in 2020 and is forecasted to increase at a CAGR of over 16% from 2021 to 2027.
Concerning the rising inclination toward automated testing, Quality Assurance (QA) automation experts need to be fast, capable of detecting bugs promptly, and flexible in solving problems. However, in contrast to predecessors, having manual testing knowledge is not enough for testers nowadays. Otherwise, it’s crucial for automation testers to have sufficient skills related to automated testing to take full advantage of this method.
Let’s figure out the automation testing skills needed to be an effective and successful QA automation engineer in 2024!
Roles in a QA Automation Testing Team
Automation testing has become a cornerstone for many industries, especially the BFSI sector, as it streamlines customer service processes and helps reduce any errors or defects related to humans. A typical QA automation engineer is often responsible for creating automated tests to verify the functionality of the software and mobile apps through developing scripts, implementing testing protocols, and delivering efficient solutions for test automation.
Depending on clients’ specific demands, the project’s complexity, and the objectives set, a QA automation team may combine different roles. Common roles that should be included in a QA automation testing team:
A test automation engineer designs, develops, and implements automated testing solutions to streamline and enhance the efficiency of software testing processes.
Automation testers should be able to use programming languages and testing frameworks to create scripts that simulate user interactions with software applications. These scripts are then executed to automatically perform repetitive and complex testing tasks, allowing for quicker and more accurate identification of issues in the software.
A QA lead is responsible for developing a test automation strategy and the product’s final quality. They also oversee and guide a team of automation testers to ensure the effective implementation of automation testing processes and the delivery of high-quality software.
This is one of the important roles in the automation testing team. The role of performance test engineer includes providing guidance on effective performance testing strategies throughout the entire software development lifecycle, establishing the test framework, formulating test plans aligned with business needs and customer specifications, and overseeing the work of junior and mid-level professionals.
Challenges that Automation Testers May Face
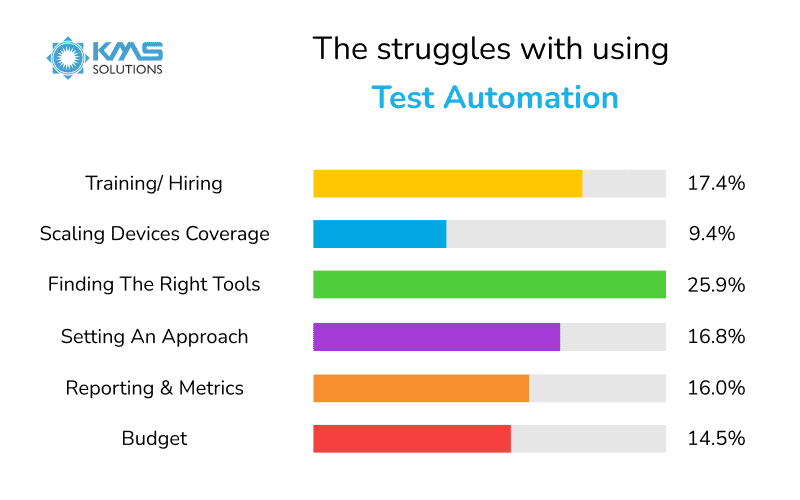
Although switching from manual testing to automated testing can have many advantages, this modern testing method also results in obstacles for the QA team. According to the State of Test Automation 2020-2021 Survey by Kobiton, the inability to find appropriate automation tools and the lack of key skills for automation testers are significant pain points that automation testers face. If you’re unable to overcome these struggles, automation testing won’t deliver the best values that it should.
Some challenges that the QA team may face when attempting to execute an automated testing strategy include:
Can’t find the right automation tools
Choosing the appropriate test automation tools is relatively tricky since there’s a diverse array of both licensed as well as open-source tools available. Although each test automation tool has its own benefit, not every method is suitable for your project. Many teams get stuck at this stage since their chosen tools cannot provide complete test coverage or they lack some needed skills for automation testing to use the tool effectively.
Unable to define the test automation approach
Without the right test automation strategy, technology will lose its effectiveness. This is comparable to a body without a brain. Choosing the proper strategy is another critical obstacle in automation testing since test engineers may find it difficult to build a plan with various dimensions to consider. To address this struggle, developing automation testing frameworks at the beginning of the testing process is worth considering.
Have insufficient technical skills for automation tester
Several test automation tools only work well when manned by skillful test engineers, who can design automation frameworks, and build test scripts and solutions accurately. It’s a misperception that manual testers can carry out the automation tools effectively without proper training.
Despite the test script record and playback features offered by most testing tools, automation testing efforts may fail if QA engineers cannot use these tools to their full potential.
Some of the Most Common Skills Needed in Automation Testing Project
As we progress into 2024, the skill set needed for Automation Testers has expanded, requiring a mix of technical expertise, analytical thinking, and soft skills. These skills not only empower them to build strong automated testing frameworks but also to work efficiently with cross-functional teams, embrace new technologies, and drive continuous improvement in development processes.
Programming and Scripting Skill
- Languages: Proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, or C# is crucial.
- Scripting: Ability to write scripts to automate test cases and frameworks.
- Code Understanding: Knowledge of data structures, algorithms, and object-oriented programming concepts.
Understanding of Software Development and QA Processes
- SDLC Knowledge: Thorough understanding of the software development lifecycle.
- QA Methodologies: Familiarity with various QA practices and standards.
- Agile and DevOps: Knowledge of Agile methodologies and DevOps practices, including CI/CD.
Debugging and Troubleshooting
- Issue Identification: Quickly identifying and diagnosing test failures.
- Log Analysis: Analyzing logs to understand application behaviour.
- Problem Solving: Developing solutions to overcome testing challenges.
Analytical and Logical Thinking
- Test Design: Designing effective and comprehensive test cases.
- Result Analysis: Interpreting test results to identify trends and issues.
- Optimization: Continuously improving testing processes based on data.
Communication and Collaboration
- Reporting: Clearly communicating test results and their implications.
- Teamwork: Working effectively with cross-functional teams.
- Documentation: Creating detailed documentation for test cases and frameworks.
6 Must-Have Skills for a Top Automation Tester
Automation testers are vital to cross-functional teams. Their responsibilities include designing and writing automation scripts, debugging test cases, using automation frameworks, undertaking testing environment setup, probing into problems that arise post-testing, and many more.
Since automation testing is no longer a strange term, testers should be well-equipped with specific skills and knowledge to overcome the struggles arising during the testing process.
1. Proficiency in Programming Languages
Although coding knowledge is not required for all QA engineers, it’s still integral for automation testers to provide successful software test cases. Having basic programming knowledge will not only simplify your effort in writing automation test scripts but will also enhance your communication with the developer. Additionally, once unit testing is completed, you can have the capability to participate in in-depth functionality testing. When deciding to learn programming languages, here are aspects that automation testers can expect to improve:
- Designing the automation testing frameworks
A testing framework is a set of guidelines for creating and developing test cases. Designing an automated framework will help you maintain coding standards across the library and increase test cases’ quality, speed, and accuracy. This step will require you to have a sufficient understanding of C#, Java, NodeJS, Python, SQL, HTML, and CSS. The programming language you choose for testing should depend on the languages that developers use in the project.
Writing the testing scripts
The automation tester should create the testing scripts with the purpose of saving both time and effort during the test creation and the test execution process. Though it is no longer essential to write your automated scripts by using scriptless test automation, it’s still beneficial to understand the fundamentals. Python and JavaScript are top programming language options for newbie automation testers due to their user-readable syntax and ease of use.
2. Sufficient Knowledge of Automation Tools
There’s a vast selection of automation testing tools available in the market that can bring significantly superior benefits to a business. To flourish in the area of automation testing, testers are required to have a thorough grasp of and experience using automation tools. Moreover, they need to know which tool will work best for the particular project because each job may require different testing types and technologies to support it. Choosing the right tool also ensures Return on Investment (ROI) yielding from automation testing is achieved.
Before picking a particular tool, the test engineer should examine the pros and cons of each option. Here’re some widely-used tools in the market today:
- Katalon Studio
Katalon is an end-to-end test automation tool that facilitates automated tests for Web, APIs, Windows desktop, and Mobile apps, supplies test records, and reports test analytics.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
- Selenium
Selenium is a suite of open-source testing automation tools that’s become the industry standard in quality assurance.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Appium
Similar to Selenium, Appium offers an open-source test automation framework. However, it concentrates mainly on the automation of mobile testing,
Pros | Cons |
|
|
3. Clearly Understand Business Requirements
Whether your car is experiencing a problem and you’ll need to take it to the service center, before fixing the vehicle, the mechanic will ask you about the current issue and any previous vehicle issues that were resolved during the last servicing, along with any part that would have to be replaced. By doing that, the mechanic can understand precisely what happened with the car and have the appropriate solution accordingly.
Similarly, the qualified automation testers must know the software inside out, both front-end and back-end levels, at the beginning of the testing phase. They should be familiar with:
- The programming language used in the whole project.
- Browser or device requirement in which the app will be accessed by the end-users.
- All the modules and features that will be released.
- APIs and web services connected to the system.
- Databases are used for keeping user data and back-end information.
- Manual testing may need to be executed while the testing phase begins.
- Test execution compilation delivery date and expected release timelines.
4. Well-versed with Test Management Tools
Automation testing’s main objective is to reduce testing time while ensuring the quality of test cases. Having knowledge of automation tools is not enough; you’re also required to be expertise with management tools to deliver quality bug-free software in time.
Test management and bug-tracking solutions aid in streamlining testing, addressing errors based on priority, tracking testing, obtaining real-time reporting, and preventing security risks. When used effectively, test management tools can help reduce time wastage and accelerate the testing process for a better cycle. In addition, its scalability enables the effortless exchange of information among the team members.
Some test management tools that QA automation engineers should have in 2024 include:
- TestRail: a software tool designed for test management, assisting teams in effectively overseeing and monitoring software testing activities.
- Zephyr: a test management solution, often integrated with JIRA to provide customizable dashboards for real-time visibility and advanced testing reports.
- PractiTest: offers a broader range of test management functionalities, including requirements management and defect tracking.
5. Expertise with Agile, DevOps Methodologies & Continuous Delivery
As a result of rising demands for accelerated automation testing, new-age Agile and DevOps models are gradually replacing the waterfall model.
Due to the rapid changes inherent with Agile methodology, it’s vital to have an automated testing strategy in place. Automation testers may automate a module’s test scripts to adapt to customers’ ever-changing requirements. In contrast to the waterfall model’s case, in which testing and development teams may be separated by clear boundaries, Agile and DevOps emphasize intense synchronization, collaboration, and the use of cross-functional teams.
These methodologies mean a change of culture, indeed, but they also demand additional skills such as:
- Basic knowledge of networking and UNIX/ Shell scripting.
- CI/ CD pipelines with tools like GitLab and Jenkins.
- Performance testing tools such as Gatling and JMeter.
- Cloud services such as AWS and MS Azure.
Therefore, participating in an Agile, DevOps, CI/CD pipeline might speak volumes about your ability to integrate seamlessly with the organization’s teams.
6. Possess Analytical Skills
A proficient software tester needs to possess strong analytical skills, enabling them to break down intricate systems into smaller components and gain a clear understanding of the underlying code.
Additionally, these analytical capabilities are crucial for formulating improved test cases, ultimately augmenting the overall efficiency of the system. The primary responsibility of a tester involves pinpointing issues and devising optimal strategies to address them. Achieving this requires an analytical mindset, allowing them to thoroughly analyze problems, identify bugs, and address security vulnerabilities.
Certifications for Automation Testers
1. ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board)
- ISTQB Certified Tester – Foundation Level (CTFL): A beginner-level certification that provides a solid understanding of testing principles and practices.
- ISTQB Certified Tester – Advanced Level: Offers specialized tracks such as Test Analyst, Test Manager, and Technical Test Analyst.
- ISTQB Certified Tester – Test Automation Engineer: Focuses specifically on automation skills and best practices.
2. Certified Software Test Automation Specialist (CSTAS)
Offered by the International Institute for Software Testing, CSTAS certifies the competency in designing and implementing test automation frameworks and tools.
3. Certified Selenium Professional
Various institutions offer this certification, validating skills in using Selenium WebDriver for automated testing.
4. Certified Agile Tester (CAT)
This certification covers agile testing methodologies and practices, ensuring testers can effectively work in agile development environments.
5. AWS Certified DevOps Engineer
Validates expertise in provisioning, operating, and managing distributed application systems on the AWS platform. It’s particularly useful for testers involved in CI/CD and automation.
6. Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
Focuses on DevOps principles and practices on the Microsoft Azure platform. It includes automation, CI/CD, and collaboration best practices.
How Can Automation Testers at KMS Solutions Help You?
Challenges are unavoidable in every industry, including automation testing. Automation testers must be multiskilled and most practically have an assortment of technical expertise, domain knowledge, and skills for automation testing that enable them to get over challenges and deliver quality software promptly.
At KMS Solutions, our QA engineers not only own practical experience, domain knowledge, exceptional digital capabilities but also show their dedication to bringing success to our clients through real projects:
- GIC Real Estate adopts test automation
- Improve the testing process of Maxis with automated testing
- Support HDBank’s QA Team gained In-Depth Knowledge of Katalon Automation Testing Tool
- Accelerate Testing Process and Optimize Testing Resources for Maxis – a leading telecommunication in Malaysia
- TPBank successfully boosted the performance of its systems for mobile users growth
Moreover, KSM Solutions’ talents have proven their capabilities in Test Automation consulting, training, implementation, and maintenance. As executing automation testing is not an easy task, having a team of fully skilled testers can help your business ensure the efficiency of the software development cycle. Discover how our Automation Testing services can enhance your testing strategy today!
Leave your information here if you want to expand your testing team or accelerate your testing process.












