Back in 1865, the term business intelligence (BI) was first used to describe a banker who gained an advantage by gathering market insights ahead of his competitors. Today, BI implementation has become a cornerstone of success. Small financial institutions now can leverage data to understand customer demographics, behaviors, and preferences to tailor their services more effectively.
For larger banks and financial organizations, BI implementation can support in-depth analysis of past performance, provide insights into the current business landscape, and help forecast emerging market trends, empowering strategic decision-making for even years ahead.
To stay ahead of competitors, leading banks invest heavily in BI, transforming data into their most powerful competitive advantage. Let’s explore how to implement BI effectively with our guideline!
Key Benefits of BI Implementation in the Banking Industry
As the banking industry operates in a highly dynamic and data-intensive environment, adopting BI can bring a wealth of benefits that help banks and financial organizations optimize operations and make data-driven decisions. Below are some key advantages of BI implementation in the banking sector:
- Smarter Decision-Making: BI systems provide banks with real-time data analytics, enabling leaders to make informed, strategic decisions. By consolidating data from various departments, you can gain a holistic view of performance and market trends. This minimizes reliance on intuition and helps banks respond fast to ever-changing markets.
- Improved Risk Management: Risk assessment is critical in banking, and BI tools play a vital role in minimizing financial risks. With BI, banks can analyze historical data and predict potential risks. A leading bank, Wells Fargo, has leveraged BI-powered risk analytics to identify patterns of financial distress in borrowers, allowing them to adjust credit risk models and prevent potential defaults.
- Boosted Operational Efficiency: By implementing BI, banks can streamline internal operations by automating data analysis and reporting. For instance, branch managers can quickly access performance metrics, while loan officers can speed up credit assessments.
- Enhanced Fraud Detection and Compliance: For banks, adhering to industry standards and maintaining robust security measures are essential. BI systems can monitor transactions in real-time and flag suspicious activities; for example, HSBC has used BI-driven fraud detection algorithms to monitor millions of transactions daily.
- Predictive Analytics with Power BI: Beyond historical data analysis, BI systems leverage predictive analytics to forecast future market trends, customer behaviors, and financial performance.
Challenges When Implementing Business Intelligence

While BI offers numerous benefits and opportunities, it also comes with certain challenges that must be addressed to fully harness the power of data. Below are some of the most common obstacles and our suggested strategies to effectively overcome them.
1. Data Integration and Quality Issues
Every day, banks collect vast amounts of data from various sources, including customer transactions, loan applications, mobile banking, and regulatory reports. However, integrating this data into a unified BI system can be complex due to: data silos across different departments, inconsistent data formats, and duplicate or inaccurate data.
#Solutions: To mitigate data integration issues, banks must implement robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes and adopt data governance practices, such as multi-level access controls, to further ensure the accuracy and consistency of the collected data.
Read more: Data Integration in Practice: An In-Depth Exploration of Strategies, Frameworks, and Use Cases
2. Complex Regulatory Compliance
Unlike other industries, banks must adhere to strict financial regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR, PCI DSS, and industry-specific regulations such as eKYC/AML rules. A recent report shows that when adopting BI, banks often encounter challenges in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and protecting sensitive customer information.
#Solutions: The best practice here is integrating regulatory compliance modules into their BI platforms and conducting regular security audits. Partnering with a technology partner that has domain knowledge in financial services is also a possible way to ensure BI implementation aligns with changing regulations.
In KMS Solutions, we comply with PCI DSS, SOC 2 Type II, and hold Certified Banking Domain Professional (CBDP) credentials to offer trusted digital banking systems.
3. Security and Data Privacy Concerns
With cyber threats on the rise nowadays, securing financial data is a top priority for banks. However, implementing BI systems requires granting access to a large volume of sensitive corporate and customer data, which will be processed and analyzed through various BI tools. Throughout these interactions, it is essential to ensure that this data remains secure, protected from unauthorized access, potential breaches, and regulatory violations.
#Solutions: To strengthen data security and privacy, banks and financial institutions should adopt multiple protective measures, including multi-tiered access controls, robust data encryption, advanced cybersecurity solutions, and routine security audits. These practices help safeguard critical information while maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.
4. Lack Specific Technology Skills
BI implementation is not a simple plug-and-play process; it requires deep technical knowledge in data architecture, data analysis, data visualization, and BI tool management. However, many banking institutions, especially those with a traditional operational model, often struggle to find or retain professionals with the expertise needed to effectively run and manage BI systems. Moreover, investing in training programs can be costly and time-consuming. Smaller banks with limited budgets may find it difficult to allocate sufficient resources.
#Solutions: To successfully implement BI and derive maximum value from it, banks can engage with trusted technology partners to assist in the initial stages or the full process of BI implementation. By partnering with KMS solutions, regional banks and financial institutions can deploy a large-scale BI solution to streamline reporting and data analysis operations across multiple branches.
10 Key Steps for Business Intelligence Implementation in Banking
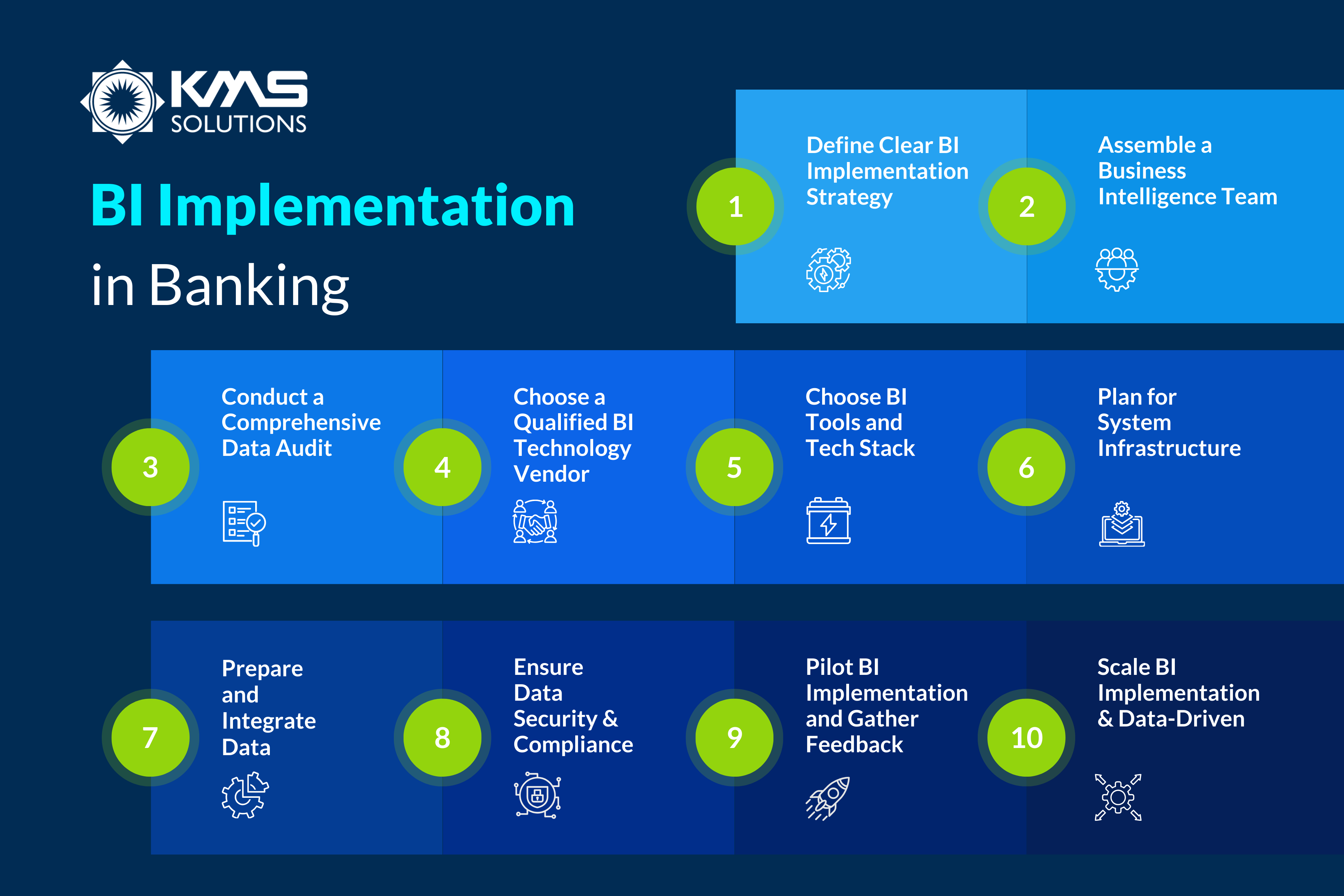
The implementation of BI in banks is a complex process that requires careful planning and strong technical execution. Drawing from industry best practices and real-world experience, our BI experts recommend a structured process to ensure effective BI implementation for banks.
1. Define Clear BI Implementation Strategy
The foundation of a successful BI implementation starts with a well-defined strategy aligned with the bank’s overall business goals. Without a clear strategy, BI initiatives can become fragmented, leading to wasted resources and low adoption rates.
Thus, when building a strategy for adopting BI, you should start by answering these questions:
- What are your software problems that BI can solve? (e.g., streamline operations, lower customer churn, or optimize costs)
- What BI resources do we currently have? (e.g., available data sources, responsible departments, number of IT teams)
- Are there any additional data and systems required to support your BI goals?
Next, you should set measurable objectives and visualize what your required BI system should look like. With these details in place, you can proceed confidently by creating a structured BI implementation roadmap with defined timelines, budgets, and deliverables.
2. Assemble a Dedicated BI Team
With a solid plan in place, the next step is to appoint a team to execute it. BI implementation is not merely an IT project—it requires collaboration between business units, data specialists, IT, compliance, and senior management. Therefore, banks should establish a cross-functional team responsible for driving the BI initiative.
Essential roles in the BI team should include: project manager, data analysts and engineers, IT & security experts, and quality assurance. The key thing here is clearly outlining each team member’s duties to prevent overlaps and gaps.
By partnering with a trusted IT service provider like KMS Solutions, banks can quickly access an experienced and dedicated BI team without the need to spend time and resources on recruiting and training. At KMS Solutions, our development team is fully equipped with the essential BI tools, proven methodologies, and deep industry knowledge to help you implement and optimize your BI systems efficiently.
3. Conduct a Comprehensive Data Audit
Before launching BI initiatives, banks must assess the data they already possess. Typically, data in banks is scattered across different systems like core banking, CRM, loan management, and customer support platforms, often stored in incompatible formats.
A general data audit process often includes:
- Identify all data sources across the bank.
- Evaluate data quality: completeness, accuracy, consistency, and timeliness.
- Detect and address data silos.
- Analyze data volume, structure, and format.
4. Choose a Qualified BI Technology Vendor
Implementing a BI system requires advanced technical skills and specialized tools. While building an in-house BI team is an option, it demands a full-scale department comprising data architects, database administrators, ETL developers, data quality analysts, and project managers—resources that many banks may not have readily available.
Hence, outsourcing BI implementation is often a more efficient and cost-effective approach for financial institutions. When choosing a vendor, it’s crucial to ensure they have industry experience, a highly skilled team, expertise in key technologies, and a proven track record of delivering quality solutions at a competitive price. At KMS Solutions, we specialize in managing complex BI projects for the BFSI industry, ensuring timely delivery and cost-effective solutions that align with business goals.
5. Choose the Right BI Tools and Technology Stack
The BI technology market offers various solutions ranging from self-service BI platforms to advanced analytics and machine learning systems. To choose the right solution, banks should consider both functional requirements and non-functional factors. Here are key things to evaluate when choosing BI tools:
- Functionality: Data visualization, dashboarding, reporting, real-time analytics.
- Integration capabilities: Compatibility with core banking systems, cloud platforms, APIs.
- Security features: Encryption, user access control, compliance readiness.
- Scalability: Support for growing data volumes and user base.
6. Plan for Infrastructure
Two key infrastructure components are crucial for BI implementation: data storage and the BI platform.
Traditional on-premise databases are often outdated and lack the flexibility to handle growing data volumes. Many organizations now opt for Enterprise Data Warehouses (EDWs), which allow centralized storage and efficient processing of data from multiple systems (ERP, CRM, HRM, etc.).
Similarly, local BI platforms are increasingly being replaced by cloud-based or hybrid solutions that offer better scalability, lower costs, and easier maintenance.
7. Prepare and Integrate Data
After selecting BI tools and planning infrastructure, the next step is data preparation and integration. This is often the most time-consuming phase, consuming up to 80% of the BI implementation effort. The process of data preparation generally comprise:
- Extract data from multiple internal systems (CRM, ERP, Core Banking).
- Transform and clean the data to ensure consistency and relevance.
- Integrate external data sources (market data, social media feeds, economic indicators).
- Load the data into a centralized Data Warehouse or Data Lake.
8. Ensure Data Security and Compliance in Banking System
Since banks and financial institutions deal with highly sensitive financial and personal information, data security has become a top priority in BI projects. This step is compulsory for BFSi businesses to implement multi-layered access controls, encrypt sensitive data, and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
9. Pilot BI Implementation and Gather Feedback
Before rolling out BI across the organization, it’s advisable to conduct a pilot implementation. This allows banks to test BI capabilities, validate data accuracy, and collect feedback from end-users. Key best practices include:
- Select a specific department or use case (e.g., credit risk analysis, customer segmentation).
- Involve end-users early to ensure usability.
- Measure results against pre-defined KPIs.
- Adjust data models, dashboards, or processes based on feedback.
- Continuously monitor performance, identify problem areas, and refine the system to maximize its impact.
10. Scale BI Implementation and Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Once the pilot proves successful, the bank should scale BI implementation across other departments and processes. However, successful BI adoption is not just about technology—it requires nurturing a data-driven culture.
Conclusion
Implementing business intelligence in banking is a strategic move that enhances decision-making, improves operational efficiency, and strengthens customer relationships. However, the process is complex and requires meticulous planning, the right technology, and a skilled team to ensure success.
By following our suggested key steps, banks can maximize the value of their BI investments. At KMS Solutions, our BI experts can provide end-to-end BI implementation services, from strategy development and data integration to advanced analytics. Our expertise ensures that banks can unlock actionable insights, drive innovation, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market. Contact us today and let our experts be your trusted BI partner and help you transform data into a powerful asset for long-term success.











