Open Banking API Integration is at the heart of the revolution currently transforming the financial industry. But with great power comes great responsibility—particularly in terms of compliance. This article offers a comprehensive guide to navigating the complexities of open banking API integration, highlighting the innovative strategies and best practices that can help financial institutions thrive in this new era.
1. What Is An Open Banking Api Integration?
Open banking API integration involves connecting and synchronizing different financial systems, such as banks, non-bank financial institutions, and third-party service providers, through standardized Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These APIs enable the secure exchange of financial data and services, allowing customers to share their information with authorized third parties and gain access to a broader array of financial products and services.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how open banking API integration typically works:
- Customer Consent: The process begins with the customer giving explicit consent to a third-party provider to access their bank data. This consent is crucial and regulated to ensure privacy and security.
- API Request: After receiving consent, the third-party provider submits an API request to the customer’s bank. This request specifies the data or services they need to access.
- Authentication and Authorization: The bank authenticates the third-party provider and verifies the customer’s consent. This is critical for security and ensures only legitimate requests are processed.
- Data Sharing: Upon successful authentication, the bank shares the requested data with the third-party provider through the API. This data could include transaction history, account balances, or other relevant information.
- Service Delivery: The third-party provider uses the accessed data to deliver innovative financial services to the customer. These services can range from budgeting apps and payment services to personalized financial advice.
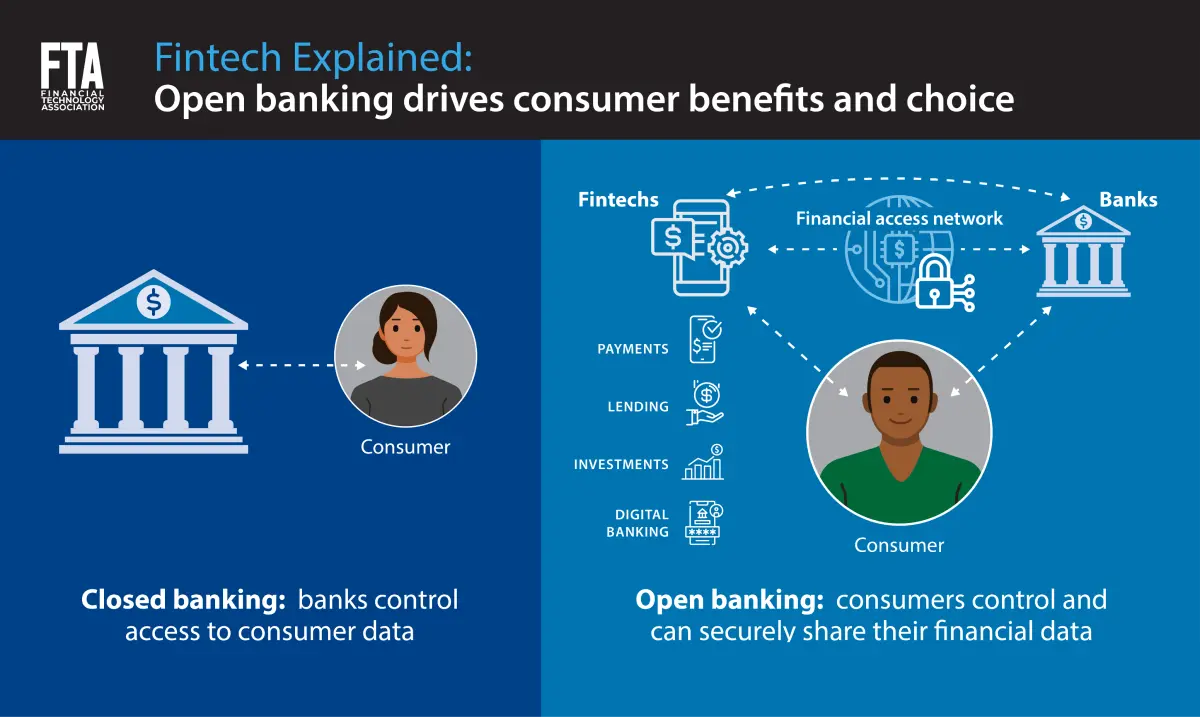
2. How Open Banking API Works
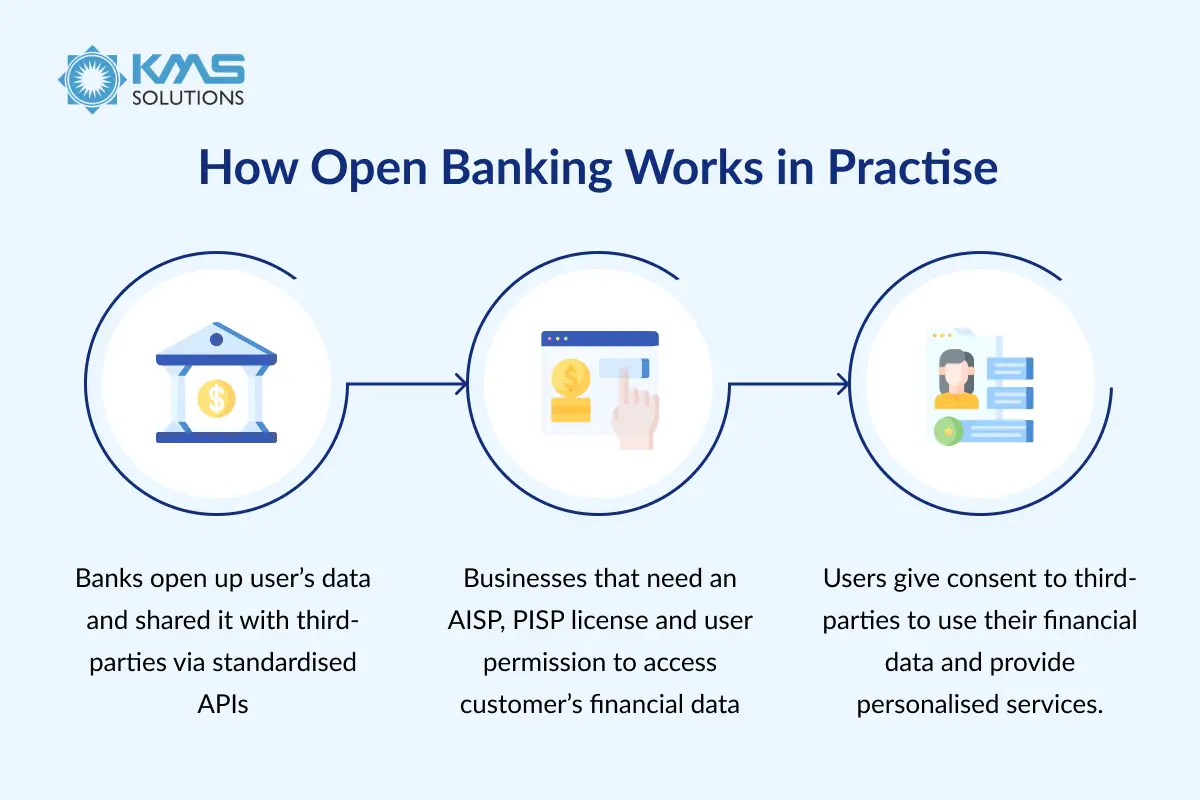
What the Banks Do – API integration in banking
With the introduction of the Payment Services Directive (PSD2), banks are now obligated to share consumer data through an API that licensed third parties can access. Interestingly, all major Australian banks are compliant with open banking.
How Businesses Get Registered – API integration in banking
Companies need an AISP or PISP license to access customer financial data. Once authorized, they can use Open Banking APIs to access the data securely.
What the Customer Sees
Consumers grant consent for third-party access, enabling more personalized services. Payments are processed directly from bank to third-party app, streamlining the transaction without intermediaries
3. What’s the Difference Between Open Banking And Banking API?
When discussing the modern financial landscape, Open Banking and Banking APIs have become two fundamental components shaping the future of banking services. While both terms may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes in transforming how banks, fintech companies, and other third-party providers operate.
| Open Banking | Banking API | |
| Overview | A compliance-based program that permits third-party financial service providers to obtain consumer banking information, provided that consumers give their approval | A technical interface that allows two software applications to communicate, often enabling data exchange or service integration |
| Primary Purpose | To enable financial transparency, innovation, and competition by securely sharing financial data between banks and third-party providers (TPPs) | To provide seamless integration and functionality between banks and external systems or applications, enhancing banking operations |
| Regulation | Governed by strict regulatory frameworks, like PSD2 in the EU and Open Banking Regulation in the UK, ensuring security, consumer consent, and data privacy | Not necessarily tied to a regulatory framework; APIs may be proprietary or open, depending on the bank or organization offering them |
| Scope | Broader in scope, covering multiple financial services like payments, account aggregation, and lending across different financial institutions | Narrower in scope, often designed for specific purposes (e.g., transaction processing, account management, payment gateways) |
| Data Access | Provides access to consumer financial data from multiple institutions, with the customer’s consent, enabling third parties to build services on top of that data | Can provide access to specific data or services (such as payments or account info) from one or more institutions, often used within a single bank’s ecosystem |
| Use Cases | Enables services like multi-bank aggregation, personal finance management apps, account-to-account payments, and lending platforms | Enables specific use cases like transferring funds, checking balances, making payments, or integrating with third-party financial services |
| Third-Party Ecosystem | Enables a large ecosystem of fintechs, startups, and service providers to build on top of bank data | May support external partnerships, but it’s more often used to integrate specific functionalities within a bank’s own system |
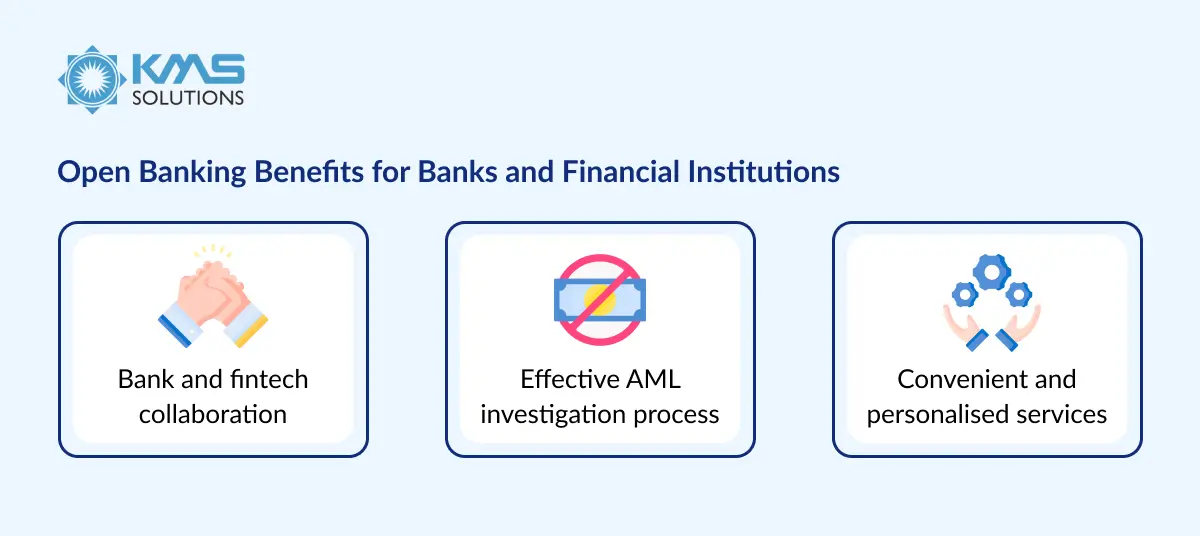
Benefits of Open Banking - Bank api integration
1. Benefits for Banks & Financial Institutions:
Fintech Collaboration
- Helps banks stay relevant in evolving financial landscape
- Enables access to modern technology trends
- Allows banks to leverage innovative infrastructures
- Enriches financial services offerings
AML Investigation Enhancement
- Access to real-time financial data
- Faster analysis capabilities
- Better detection of suspicious transactions
- APIs enable direct comparison of customer-provided information with real-time data
Customer Experience
- Provides effortless and extended data access
- Enables personalized financial recommendations
- Simplifies e-KYC process
- 90-day access window for customer verification
2. Benefits for Organizations:
Financial Advantages
- Reduced service charges
- Access to alternative payment methods beyond cards
- More payment service provider options
- Competitive rates from various providers (e.g., eWay, ANZ eGate, Square)
Conversion Improvements
- Streamlined payment processes
- Faster transaction processing
- Real-world example: Axi Trading platform achieved $2.5 trillion in trades (2020)
- Integration of multiple PSPs for better service
Loan Access
- Simplified credit risk evaluation
- Direct access to financial data through secure APIs
- More informed lending decisions
- Real-time comprehensive financial information

3. Benefits for Customers:
Data Control
- Complete authority over financial data
- Secure login details and password protection
- Control over third-party access levels Enhanced data security and privacy
Financial Management
- Consolidated view of multiple accounts
- Better budgeting capabilities
- Improved expense monitoring Access to tailored financial advice
Service Improvements
- No need for branch visits
- Elimination of manual transaction file uploads
- Time-saving processes
- Access to competitive services due to market competition
4. Open Banking Integration Use Cases - Bank api integration
This exploration delves into specific use cases of open banking integration, highlighting how these APIs are transforming the way individuals and businesses interact with financial services.
4.1 Accounting Solutions
Open banking facilitates the automation of key financial processes. For instance, companies can integrate platforms like Yapily to streamline bookkeeping and financial reporting. By leveraging open APIs, businesses can connect multiple accounts, ensuring that all financial data is synchronized in real-time.
This eliminates the need for manual data entry, allowing accountants and business owners to monitor their financial health from a single, comprehensive dashboard, thus improving accuracy and reducing errors
4.2 Loan Evaluation and Creditworthiness Assessment
Loan providers, particularly fintech startups, are using open banking APIs to enhance how they evaluate applicants. For example, Carbon, a fintech app, not only looks at a borrower’s income but also analyzes their investment portfolios, which provides a broader view of the person’s financial stability. This integration helps financial institutions assess risk more accurately and offer tailored loan products that match the customer’s financial profile.
4.3 Enhancing Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Capabilities
The growing popularity of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services in e-commerce is fueled by open banking APIs that allow for quick and reliable credit checks. E-commerce platforms can integrate open banking systems to instantly verify if customers qualify for deferred payments without requiring lengthy credit assessments.
Companies like Klarna and Afterpay utilize this technology to ensure consumers have the ability to split payments into manageable installments. This fast verification process boosts customer satisfaction and reduces cart abandonment rates, helping online retailers grow sales.
4.4 Managing Variable Recurring Payments (VRPs)
Variable recurring payments (VRPs) are another area where open banking has simplified complex financial tasks. Financial institutions, mortgage lenders, and subscription services can use open banking software to handle recurring payments such as rent, insurance, subscriptions, or mortgage repayments. Open banking enables users to set specific payment parameters, providing them with control over the timing, frequency, and amount of their recurring payments.

5. Challenges Of Open Banking API Integration
While the promise of increased transparency, enhanced customer experiences, and streamlined financial services is enticing, the road to successful integration is fraught with complexities.
- Regulatory Compliance and Security Concerns: One of the most significant challenges of Banking & Financial API integration lies in adhering to complex regulatory frameworks. For instance, the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) governs how banks must share data with third-party providers, while the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) protects cardholder data and sensitive authentication dat . Compliance with these regulations and others is essential to ensure that customer data is handled in a legally sound and ethical manner.
- Data Standardization and Interoperability: Open Banking APIs require consistent data formats for smooth integration. However, banks often have disparate legacy systems that handle data differently. The lack of a universal standard for data formatting and transmission can create friction in API communication, resulting in delays and potential errors. Developers must work to create middleware solutions or adopt standards like ISO 20022 to ensure interoperability across different platforms and institutions, which is resource-intensive and time-consuming.
- Legacy System Integration: Many traditional banks operate on outdated legacy systems that are not built for modern API integration. Integrating Open Banking APIs with these older systems can be cumbersome, requiring extensive modifications or even complete overhauls of the core infrastructure. The process of migrating to or adapting legacy systems for API compatibility not only demands substantial investment but also poses risks of operational disruptions during the transition phase.
- Customer Trust and Adoption: Many consumers remain wary of sharing their financial data with third parties, fearing potential misuse or security breaches. Financial institutions must invest in building customer confidence by ensuring transparency in how their data is handled, offering clear consent mechanisms, and providing seamless, secure experiences. Without user buy-in, even the most advanced Open Banking API implementations may struggle to gain traction.
- Technical Complexity: Open banking API integration is complex due to the need to connect and harmonize data and services across multiple financial institutions, each using different systems, data formats, and standards. This necessitates complex mechanisms for data transformation and mapping to ensure seamless interoperability. Additionally, financial institutions often adhere to unique data standards and protocols, requiring third-party providers to adjust and comprehend these differences, which can lead to compatibility challenges and extended development and testing periods. Variations in API authentication methods, data endpoints, and usage limitations also result in further challenges.

6. Best Practices for Integrating Open Banking APIs
With the right strategies in place, organizations can leverage Open Banking to innovate and stand out in a competitive market.
- Understand Regulatory Requirements: Before diving into integration, familiarize yourself with the regulatory landscape surrounding Open Banking in your region. Understanding some compliance with regulations like PSD2 in Europe or the Consumer Data Right (CDR) in Australia will guide your development and ensure your integration adheres to legal requirements, including data protection and user consent protocols.
- Maintain strong security. Implement stringent measures like encryption, authentication, and authorization to safeguard data from unauthorized access or tampering.
- Adopt a User-Centric Design: The user experience should be at the forefront of your integration. Design intuitive interfaces that make it easier for users to grant permissions and navigate through the integration. Providing clear information about what data is being shared and how it will be used fosters trust and encourages user engagement.
- Focus on Scalability: As Open Banking evolves, your integration should be scalable to accommodate future changes. Choose an architecture that allows for easy updates and integration of additional APIs. Modular designs can help in adapting to new regulations, technologies, or user demands without significant overhauls.
- Establish Strong Partnerships with API Providers: Remember to evaluate potential partners based on their security standards, API documentation quality, support services, and reputation in the market.

7. Steps to Successfully Implement Open Banking APIs
Open Banking APIs can reshape how financial institutions interact with customers and enhance service offerings. Therefore, their implementation requires a structured approach. Here are the key steps to follow:
7.1 Choose the Right Open Banking API Provider

The first step in Open Banking API implementation is to perform a comprehensive assessment of your open banking API provider. With various providers offering different services, it’s essential to pick one that aligns with your company’s unique needs.
Key factors to evaluate include security features, API scalability, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
7.2 Develop a Comprehensive Strategic Plan

Before diving into the technical aspects of integrating Open Banking APIs, it’s essential to create a well-defined strategy. This plan should outline your core business goals, detailing how Open Banking APIs will help you achieve them. For instance, if your goal is to offer personalized financial services, determine which APIs are needed to deliver that experience. Identifying the specific features you want to provide customers, as well as setting measurable objectives, will guide the integration process.
Budget allocation and resource planning are equally important in this stage. Consider the manpower, timeline, and technical resources necessary to implement the APIs efficiently.
7.3 Ensure Full Regulatory Compliance

Open Banking is governed by stringent regulations designed to protect user data and privacy, and failing to comply can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage. Therefore, ensuring that your financial app is fully compliant with all relevant regulatory standards is a must-have.
Key regulations to consider include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2), as well as local privacy and data protection laws depending on the regions where your services are offered. This step involves securing all necessary licenses, adhering to strict data-sharing protocols, and ensuring your app meets high security standards.
7.4 Focus on the User Experience

A primary goal of Open Banking API integration is to provide customers with a more seamless and enhanced experience. With this in mind, your financial app should be designed to offer an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface. Users expect fast, reliable, and straightforward interactions when managing their financial data, so it’s important to prioritize user-centered design principles.
Additionally, the app should be optimized for various platforms, such as mobile, desktop, and tablet.
7.5 Test, Iterate, and Improve

Once your Open Banking APIs are integrated, thorough testing is essential to guarantee performance, security, and usability. This phase involves functional testing to ensure the APIs perform as expected, security testing to safeguard sensitive financial data, and performance testing to ensure the system can handle peak loads and high transaction volumes.
Automated testing tools can help speed up this process and improve accuracy by running large-scale tests efficiently. After testing, it’s equally important to collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement. This may include user interface adjustments, performance enhancements, or additional features based on user demand. Continuous improvement is key to maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and ensuring that your app remains at the forefront of innovation in the financial industry.
8. Integrating Open Banking APIs with KMS Solutions
For businesses looking to harness the potential of Open Banking, partnering with KMS Solutions offers a multitude of benefits. Here’s a closer look at why integrating Open Banking APIs with KMS Solutions is a strategic move for any organization.
- Domain Expertise: At the core of KMS Solutions is a dedicated team of experts with extensive experience in Open Banking integration. Their deep understanding of the industry means they can guide businesses in selecting the right Open Banking APIs tailored to specific needs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: KMS Solutions is committed to delivering a seamless customer experience. By leveraging Open Banking APIs, KMS enables businesses to connect disparate systems efficiently, significantly reducing integration time. This swift and streamlined process minimizes disruptions, allowing customers to enjoy enhanced services without the usual friction.
- Rigorous Compliance and Security: Navigating the complex regulatory environment of Open Banking can be challenging. KMS Solutions takes compliance and security very seriously, utilizing the latest technologies to protect customer data. Their proactive approach ensures that all integrations meet applicable regulations.
- Proven Track Record of Success: With a history of helping companies of all sizes achieve their integration goals, KMS delivers exceptional value to over 130 clients globally. Their extensive experience and case studies underscore their capability to develop and implement Open Banking solutions that drive business growth and efficiency.
To conclude, integrating Open Banking APIs with KMS Solutions presents a unique opportunity for businesses to stay ahead in a competitive market. KMS Solutions stands ready to support organizations in harnessing the power of Open Banking, fostering innovation and delivering exceptional service to customers.











