By building a digital banking model, banks can change the way all of their functions work, be it relationship management, risk & compliance, IT, or distribution. The result is that they can deliver a seamless customer experience and automate processes while improving profitability. However, there’s no all-in-one solution. Only when banks successfully digitize all of their functions will this digital banking model be built.
In this article, we will offer a reference model for digital banking – one that is built around banking value streams.
The Stacked Digital Banking Model
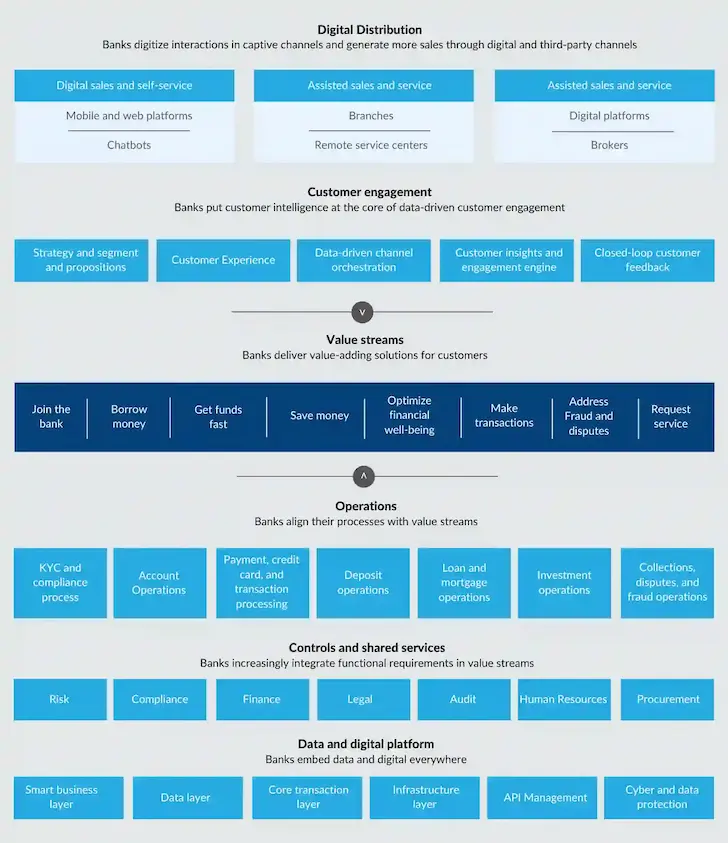
This end-to-end digital banking model is stacked with layers of capabilities similar to technology architecture, and these capabilities work together seamlessly.
The top stack is digital distribution, where banks create a higher level of customer engagement and service via owned and third-party channels. The major challenge for this layer is to enable digital sales and modernize relationship management through remote and digital channels. For example, with mobile and web applications and chatbots, customers can access and use banking services anywhere and at any time.
The next layer, customer engagement, has customer intelligence as the key enabler. All the components of this layer work together to provide banks with a deep understanding of customer’s preferences and behavior. Centering on customers, this layer is essential to digital marketing and cross-channel customer experience.
In the value streams, banks create and deliver value-adding solutions that together lead to the outcome that customers demand. In the digital banking model, value streams are the core where all other layers are organized around.
The layer of operations involves typical operational processes such as account, loan & mortgage, deposit, and KYC & compliance. The only distinction is that they are closely aligned with the value streams.
Read more: What are the Benefits of Digital Transformation to Banking businesses?
Digitization is also a must for controls and shared services, where banks would integrate functional requirements in value streams.
The data and digital platform act as the foundation of the stack. To enable ready access to data analytics by all other layers, the data and digital platform must include a single democratized data layer.
Digital Distribution
Today’s customers have become more comfortable using both physical and digital banking channels. For example, one could use one channel to pay bills but another to ask for advice or look for new products. Also, customers tend to access banking services through both the bank’s proprietary channels and third-party platforms. This behavior has a large impact on both sales and relationship management.
Digital Sales
There are customers who prefer purely digital interactions. In order to stay relevant, banks must bring fully digital products and services to these digital-savvy customers. Too often, banking apps are designed solely for customers to make transactions and access account information. By allowing customers to not only research but also buy products via mobile banking app, banks can capture a substantial growth opportunity.
Assisted Sales and Services
While digitizing their operations, banks also need to augment the human element of customer interaction so that employees can create more value for customers. Banking services must be available beyond the branches and working hours, and sales staff must be able to serve customers everywhere through remote channels such as applications.
To do so, staff will need a digital workplace, where they are provided with laptops and mobile devices that simulate the in-branch experience, advanced data analytics for client analysis, plus video calls, screen sharing to reach customers via their preferred channels.
Customer Engagement
To enable customer engagement, banks need to put customer intelligence at the core of their data-driven customer management. To do so, banks need a large database for customers’ needs, behaviors, and preferences; then use this data to enhance the analytics and AI algorithms to maximize the value of every customer touchpoint.
To enable personalized segmentation, banks should adopt the outside-in approach, instead of inside-out, that focuses on customer needs. This shift requires banks to leverage advanced data analytics solutions and build remote channels that support different types of interactions and experiences for different needs. Human efforts are directed at value-adding activities such as customer service. This data-driven approach enables the shift from a customer-to-advisor to digital and human-centric customer-to-bank relationship
Operations
To automate the most repetitive operational processes is the major goal of digital banking. As a result, human effort will be invested in the thinking tasks: exceptions, strategy planning, or customer service. Automation will turn operations from a cost center to a competitive edge. This mode of digital operations will be organized around value streams, adopt the agile approach, and embrace automation.
At the core of the operation, the layer is self-managing teams. Provided with digital applications, digital platforms solutions, and tools, they are able to handle customer requests from end to end and manage the entire backlog of their day-to-day activities with full autonomy. This autonomy will ensure greater accountability as the employees’ work outcomes will be measured in terms of reliability, efficiency, and customer experience.
A Data and Digital Platform
To enhance customer interactions across digital and non-digital channels, banks need accurate, close-to-real-time customer data, which requires a modular and scalable architecture. This architecture has some characteristics.
First, it is based on a democratized data platform that multiple layers of the organization can access. Second, they are cloud-based, instead of on-premises, and can be accessed through application programming interfaces. The smart business layer must be distinct from the IT layer. They are connected by the data layer and are designed to support every value stream.
The Data and Digital platform offer numerous benefits in terms of agility, efficiency, and time-to-market. When a bank creates more customer touchpoints and interactions throughout the customer journey, it can deliver better convenience and relevance to both customers and employees.
With all the data centralized in one place, banks can unlock the potential of AI and advanced analytics, thus creating new products in weeks rather than months, enabling data-driven decision-making, and leading to excellent customer services through a single view of customers.
If you want to learn more about Digital Banking and how to embrace your bank’s Digital Transformation, subscribe to our blogs.











